The 2025 401(k) contribution limits have increased significantly, offering new opportunities to maximize your retirement savings. With the standard limit rising to $23,500 and new super catch-up provisions allowing up to $11,250 for ages 60-63, understanding these changes is crucial for your financial planning.
Table of Contents
- What Is the 2025 401(k) Contribution Limit and Why It Matters?
- Historical Context
- Key Changes to 2025 401(k) Contribution Limits
- New vs. Old Comparison
- Impact on Savers
- Real-World Case Studies
- Who Wins—and Who Might Lose
- Action Steps
- FAQs
- Conclusion & Next Steps
What Are the 2025 401(k) Contribution Limits and Why They Matter?
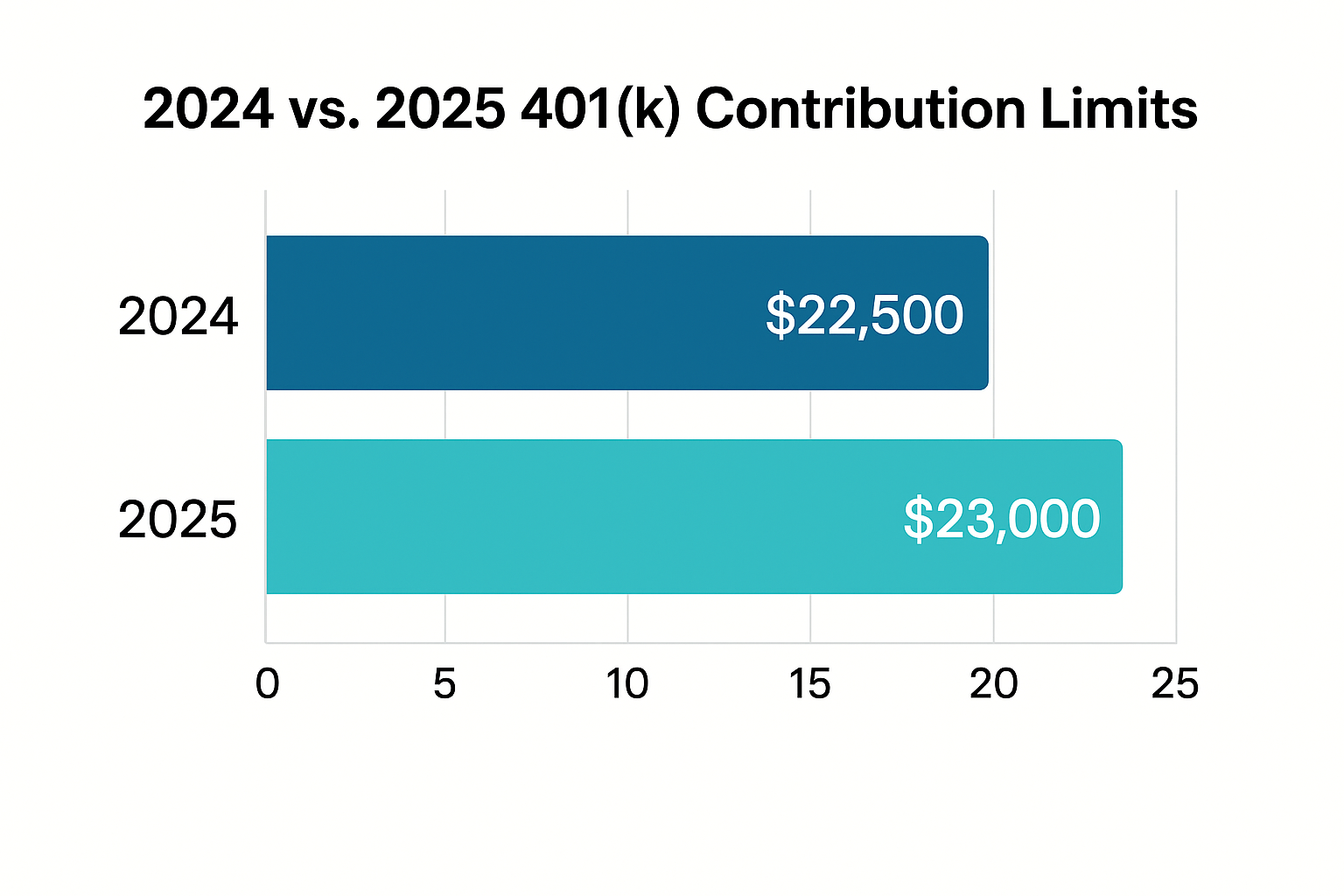
For plan year 2025, the Internal Revenue Service has increased the standard elective deferral limit for 401(k), 403(b), most 457(b) plans, and the federal Thrift Savings Plan to $23,500, representing a $500 increase from the $23,000 limit in 2024. Individuals aged fifty and older continue to qualify for an additional $7,500 catch-up contribution, maintaining the same threshold established in previous years.
The most significant development under the SECURE 2.0 Act introduces a new “super catch-up” provision allowing participants aged sixty through sixty-three to contribute up to $11,250—representing 150% of the standard catch-up amount[2]. This enhancement recognizes that many Americans begin serious retirement saving later in their careers and need additional capacity during their peak earning years.
Maximizing contributions at these elevated thresholds delivers immediate tax benefits by reducing current-year taxable income while accelerating the compounding growth of retirement savings over multiple decades. In today’s economic environment characterized by persistent inflation, elevated living costs, and uncertain Social Security projections, sheltering maximum income in tax-advantaged accounts can mean the difference between a comfortable retirement and running short of essential funds during golden years.
Historical Context
The evolution of defined-contribution plans over the past four decades has transformed 401(k) contribution limits into a critical focal point of American retirement policy. When employer-sponsored 401(k) plans were first introduced in the early 1980s following passage of the Revenue Act of 1978, the maximum elective deferral was a modest $7,000 annually.
Major legislative milestones have systematically expanded these limits through cost-of-living adjustments and policy reforms. The Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2001 established the framework for regular annual increases tied to inflation indices. The Pension Protection Act of 2006 further enhanced retirement savings opportunities while strengthening fiduciary standards for plan sponsors.
More recently, the Setting Every Community Up for Retirement Enhancement Act (SECURE Act) of 2019 and its successor SECURE 2.0 Act of 2022 have introduced innovative provisions designed to help older workers accelerate savings during their final earning years. The 2025 adjustment to $23,500, combined with the new super catch-up provision, reflects evolving recognition that traditional retirement planning models must adapt to longer lifespans, reduced pension coverage, and changing career patterns.
Key Changes to 2025 401(k) Contribution Limits
The comprehensive package of 2025 limit adjustments includes multiple categories affecting different participant populations:
- Standard elective deferral limit increases to $23,500, representing a $500 boost from 2024 levels
- Standard catch-up contributions for participants aged fifty and older remain unchanged at $7,500 annually
- Super catch-up provisions create a new tier for ages sixty through sixty-three, allowing deferrals up to $11,250 during this four-year window
- Total annual addition limits under Internal Revenue Code Section 415(c) increase to $70,000, up $4,000 from 2024 levels
- Traditional and Roth IRA contribution limits remain stable at $7,000 plus a $1,000 catch-up for those fifty and older
- SIMPLE IRA contribution limits climb to $16,500 plus a $5,250 catch-up for eligible participants
New vs. Old Comparison
| Category | 2024 Limit | 2025 Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Elective Deferral | $23,000 | $23,500 |
| Standard Catch-Up (50+) | $7,500 | $7,500 |
| Super Catch-Up (60-63) | N/A | $11,250 |
| Total Addition (≤49) | $66,000 | $70,000 |
| Total Addition (50-59) | $73,500 | $77,500 |
| Total Addition (60-63) | N/A | $81,250 |
Impact on Savers
These limit enhancements deliver measurable benefits across multiple dimensions of retirement planning:
- Tax savings represent the most immediate advantage, as full deferrals reduce adjusted gross income and lower current-year tax liability
- Compounding acceleration provides long-term wealth-building advantages as additional catch-up contributions benefit from decades of tax-deferred growth
- Behavioral incentives emerge when clear, elevated limits encourage participants to automate maximum elections
- Employer differentiation becomes increasingly important in competitive talent markets where comprehensive benefits packages influence recruitment decisions
[Chart: Tax savings vs. retirement balance growth over 10 years]
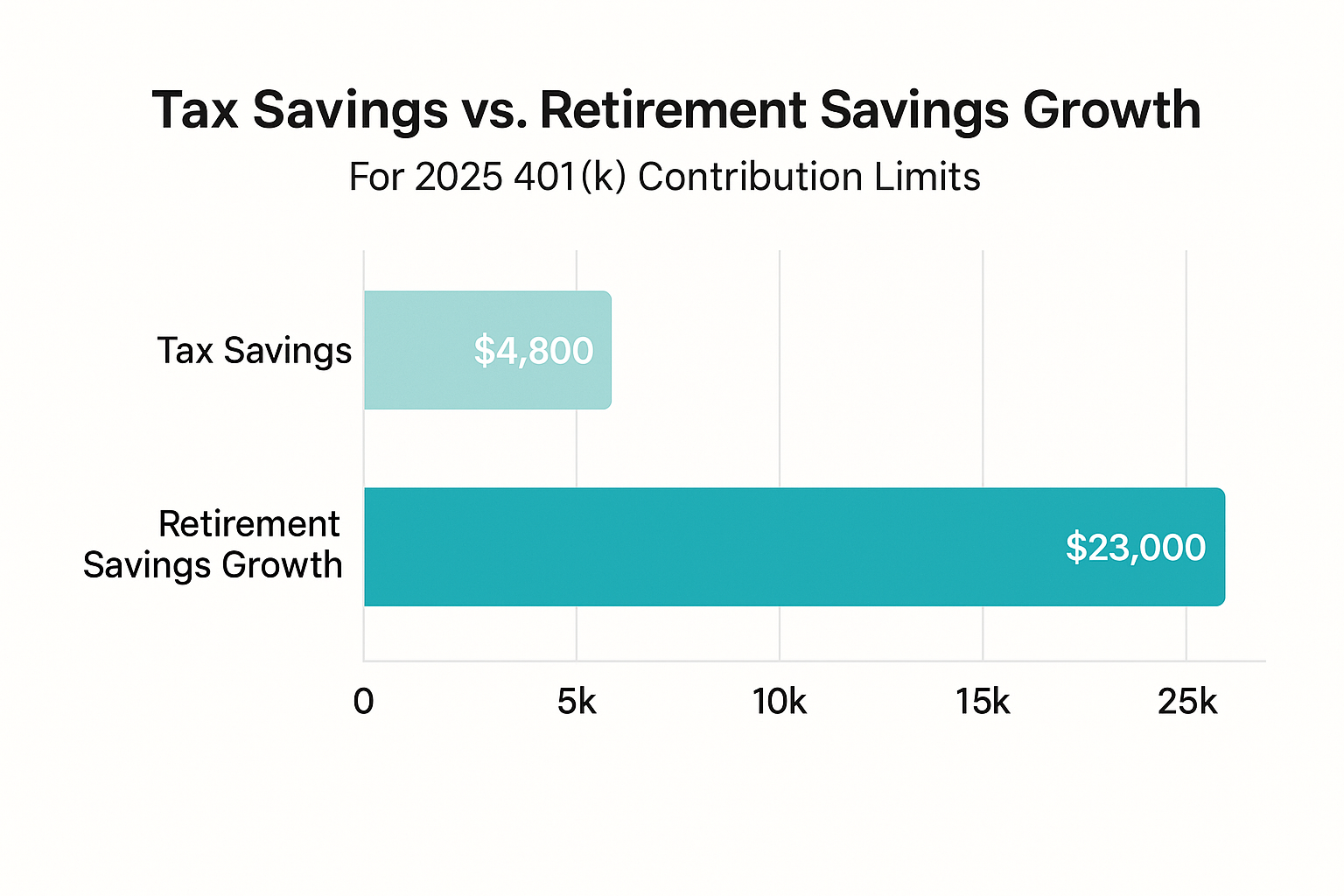
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Jane, Age 62, Healthcare Executive
Jane historically deferred $15,000 annually despite eligibility for higher amounts due to conservative financial planning and concerns about cash flow. After consulting with her financial advisor about 2025 opportunities, she automated the full $23,500 deferral plus an $11,250 super catch-up, raising total contributions to $34,750. Assuming 7% annual returns over her remaining ten working years, the extra $4,750 beyond standard catch-up levels will compound to over $42,000 by retirement. This additional accumulation provides sufficient resources to cover two full years of Medicare premiums and supplemental insurance costs.
Case Study 2: Mark, Age 57, Small-Business Owner
Mark’s S-corporation previously offered only a SIMPLE IRA due to administrative complexity concerns about traditional 401(k) plans. In 2025, he established a solo 401(k) arrangement, contributing the maximum $23,500 elective deferral plus $7,500 standard catch-up as an employee. His company simultaneously elected $50,000 in nonelective contributions to his account, bringing total 2025 additions to $81,000. Mark also executed a $20,000 back-door Roth IRA conversion, creating additional tax-free growth capacity while maintaining current-year tax efficiency through maximized deferrals.
Who Wins—and Who Might Lose
Winners:
- Late-career savers aged sixty through sixty-three who can leverage super catch-up provisions
- High-income professionals who benefit most from reducing taxable income at elevated marginal rates
- Employers adopting comprehensive catch-up provisions who gain competitive advantages in recruiting experienced talent
Potential Losers:
- Plans that choose not to adopt super catch-up provisions, leaving participants capped at lower standard amounts
- Mid-career savers aged fifty through fifty-nine who remain limited to $7,500 catch-ups
- Part-time workers, gig economy participants, and those lacking employer-sponsored plan access
Action Steps for Savers and Employers
- Update payroll systems by Q4 2024 to accommodate $23,500 elective deferrals and $11,250 super catch-ups
- Amend plan documents and summary plan descriptions to reflect SECURE 2.0 enhancements
- Communicate new limits and eligibility criteria, with targeted outreach to employees aged sixty through sixty-three
- Automate participant elections to maximize deferrals and catch-ups without manual intervention
- Coordinate with financial advisors on back-door and mega-back-door Roth strategies for comprehensive tax diversification
FAQs
Who qualifies for super catch-up contributions? Participants who attain ages sixty through sixty-three during calendar year 2025. Is super catch-up adoption mandatory for plan sponsors? No, employers may choose whether to implement super catch-up provisions. Must catch-up contributions be designated as Roth? Under SECURE 2.0 provisions, participants with wages exceeding $145,000 must make catch-up contributions on an after-tax Roth basis[5]. When must participants make elections for 2025? Contribution elections must be completed by December 31, 2025. Can participants utilize mega-back-door Roth strategies? Yes, if plan documents permit after-tax contributions and allow in-service distributions. Do employer matching contributions apply to catch-up amounts? Employer matches typically apply only to elective deferrals, not to catch-up contributions. How do 401(k) and IRA limits interact? Contribution limits operate independently, allowing participants to maximize both. How should employers track super catch-up eligibility? Payroll systems require programming to identify participants aged sixty through sixty-three.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The 2025 401(k) contribution limits—featuring a $23,500 elective deferral maximum and up to $11,250 in super catch-up capacity—create unprecedented opportunities for accelerating retirement savings. These enhanced 2025 401(k) contribution limits demand proactive implementation by plan sponsors and strategic utilization by participants seeking to maximize tax-advantaged accumulation.
Successful adoption of the new 2025 401(k) contribution limits requires automated contribution elections, updated plan documentation, and comprehensive participant education emphasizing long-term wealth-building potential. Employers implementing super catch-up provisions differentiate their benefits packages while supporting employee financial wellness objectives.
Understanding and maximizing the 2025 401(k) contribution limits is essential for anyone serious about retirement planning. Act immediately to revise payroll systems, educate eligible participants, and finalize contribution elections before year-end deadlines. These steps ensure every available dollar works toward building a secure, comfortable retirement that can withstand economic uncertainty and support desired lifestyle goals throughout your golden years.
Want to Keep Strengthening Your Finances?
If you found this article helpful, you might enjoy some of our other popular posts that dive deeper into If you found this article helpful, you might enjoy some of our other popular posts that dive deeper into saving, investing, and smart money management:
- 6 Financial Strategies to Protect Your Wealth
- Best No-Penalty CD Rates of 2025
- Best High-Yield Savings Accounts 2025
- 8 Powerful Financial Strategies Every Single Person Should Know
- The 10 Best Financial Wellness Apps That Track Mental Health in 2025
- The 10 Best Financial Wellness Apps That Track Mental Health in 2025
Keep exploring — your smartest financial years are just getting started.
Sources
- [1] IRS: 401(k) limit increases to $23,500 for 2025
- [2] Congress.gov: SECURE 2.0 Act of 2022
- [3] Congress.gov: Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2001
- [4] IRS Notice 2024-80: Retirement Plan Limitations
- Treasury, IRS issue proposed regulations on new Roth catch-up rule, other SECURE 2.0 Act provisions
This content is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice.








